Prometheus Exporter for Trucki2Sun Gateway
After lots of off-grid experiments over the past couple of years I finally installed a grid-tied solar system made up of a hand picked selection of components incl. a Lumentree Sun inverter feat. Trucki stick. This appears to be something mostly made for the German market but if you’re in Europe generally and run on 230V & 50Hz I can only recommend it so far (check your local laws blabla).
The general idea here is that due to German laws around `Balkonkraftwerke and their limitations one wants to exporter nothing into the grid and use all of the collected energy for their own needs. In order to do that you need something that constantly monitors how much is being used and then instructs the inverter to only produce just barely less power than that. The Trucki stick attached to the inverter does one of the two jobs required. It hosts a lot of data locally that I wanted retain for analysis of the efficacy of the system but it only comes with a service builtin that allows it to publish the data to a MQTT server/broker. I personally have no use for MQTT in my life and did not want to deal with the overhead which then also required a MQTT -> Prometheus bridge which is why I figured I throw some work knowledge at the problem and write my own Truck -> Prometheus exporter.
https://github.com/tzeejay/trucki2prometheus
The exporter grabs as much useful data as it possibly can from the Trucki stick and makes it available for Prometheus to scrape. If you intend to deploy this yourself, I would generally recommend to not go too crazy with the scraping intervals both on the Trucki side as well as on the Prometheus side in order to allow for enough compute resources to actually manage your inverter and power production!
I personally run the exporter off of a Raspberry Pi 5 with the help of systemd, though as the project is written entirely in Go it is very portable and should support any platform that you prefer (as long as it is supported by Go).
With all of that said, I hope that anybody but me finds any use in this tool to monitor their Lumentree Sun feat. Trucki stick nulleinspeisung operations in Prometheus without any additional MQTT overhead.
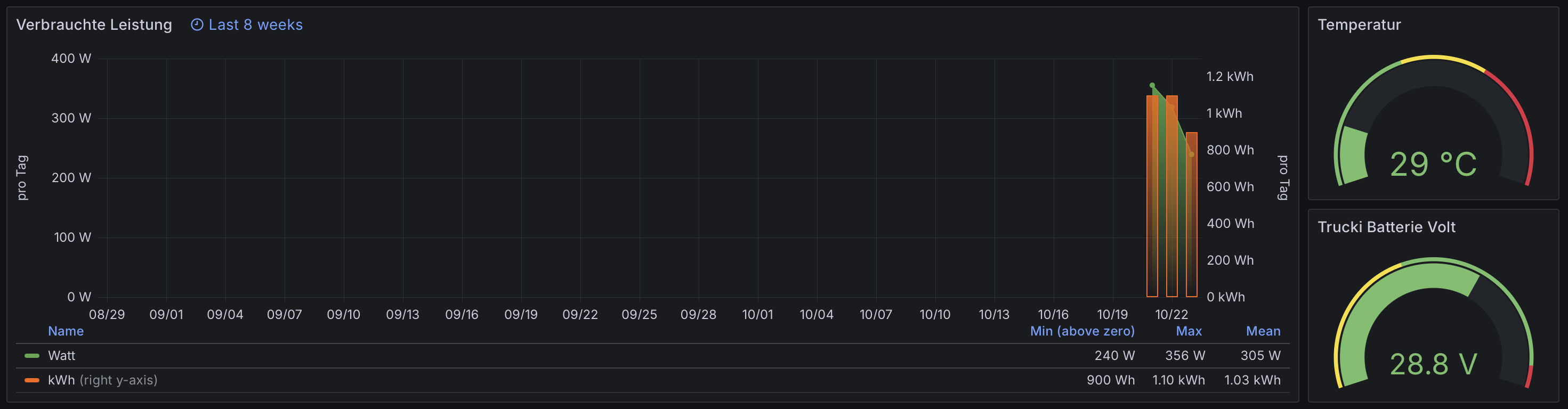
With a little bit of love you can then create pretty graphs in Grafana that look like this, I assume that I am mostly going to ignore these day to day but
Solar generation continues to absolutely delight me and I intend to keep tinkering with it. This little Balkonkraftwerk has only been operational for a handful of days but appears to be able to cover 25% of the power consumption of the house it is attached to, even as we go into winter here in Germany.
Seeing this in front of my own eyes gets me really excited for the future :)
23.10.2025
Linux Unable to Fork Processes
We’ve been busy at work upgrading a couple hundred hosts around the world to Ubuntu 24.04 LTS. While doing so we have had a subset of our hosts freak out and become almost entirely uncommunicative.
Examples of how bad things were (and hoping that the SEO gods pick this up and lead you to victory while trying to get out of your misery)
maloche ~ % ssh admin@region-2
Last login: Mon Oct 13 09:50:04 2025 from
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
/usr/bin/lesspipe: 1: Cannot fork
admin@region-2:~$ df -h
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
tmpfs 197M 19M 179M 10% /run
/dev/mapper/ubuntu--vg-ubuntu--lv 15G 7.8G 6.2G 56% /
tmpfs 982M 0 982M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
/dev/sda2 2.0G 229M 1.6G 13% /boot
tmpfs 197M 4.0K 197M 1% /run/user/1000
admin@region-2:~$ htop
admin@region-2:~$ cat /proc/sys/kernel/pid_max
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
-bash: fork: retry: Resource temporarily unavailable
4194304
admin@region-2:~$ sudo apt update
FATAL -> Failed to fork.
The FATAL -> Failed to fork. error message finally lead me down a path of something making sense. Clearly this was a resource issue but both RAM & CPU usage were fine and the disk was not out of space. This leaves file descriptors and process ids.
As it turns out for some strange reason, in our case if WireGuard was operational on the host as we started the upgrade process it would set off a process bomb that persisted across reboots.
Before the fix
maloche ~ % ssh admin@region-2
Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.0-157-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/pro
System information as of Mon Oct 13 10:43:49 PM UTC 2025
System load: 0.42 Processes: 30296
Usage of /: 53.2% of 14.66GB Users logged in: 0
Memory usage: 35% IPv4 address for ens18:
Swap usage: 0%
* Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa has reached its end of standard support on 31 Ma
For more details see:
https://ubuntu.com/20-04
Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled.
0 updates can be applied immediately.
and after
maloche ~ % ssh admin@region-2
Welcome to Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS (GNU/Linux 5.15.0-157-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/pro
System information as of Mon Oct 13 10:52:54 PM UTC 2025
System load: 0.15 Processes: 118
Usage of /: 53.1% of 14.66GB Users logged in: 0
Memory usage: 8% IPv4 address for ens18:
Swap usage: 0%
* Ubuntu 20.04 LTS Focal Fossa has reached its end of standard support on 31 Ma
For more details see:
https://ubuntu.com/20-04
Expanded Security Maintenance for Applications is not enabled.
0 updates can be applied immediately.
6 additional security updates can be applied with ESM Apps.
Learn more about enabling ESM Apps service at https://ubuntu.com/esm
As you can imagine 30296 active processes vs 118 makes a difference!
I initially stumbled over this by checking ps -ef and seeing a wall of duplicate processes all with their own pid
root 31120 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31121 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31122 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31123 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31124 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31125 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31126 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31127 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31128 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31129 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31130 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31131 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31132 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31133 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31134 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31135 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31136 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31137 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31138 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31139 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31140 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31141 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31142 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31143 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31144 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31145 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31146 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31147 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31148 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31149 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31150 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31151 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31152 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31153 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31154 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31155 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31156 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31157 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31158 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31160 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
root 31161 2 0 15:53 ? 00:00:00 [napi/wg-0]
If you see a lot of the same thing in there that you did not anticipate start by shutting that down individually. In our case we stopped it by stopping WireGuard all together on the host which took a lot of attempts to successfully complete while the host had just enough free cycles for us to get in there, so be patient. Once completed the host recovered instantly and we could continue our work. Once fully upgraded we re-enabled the WireGuard service without any further issues.
I have yet to find an explanation for what happened here. This might be a bug in WireGuard itself or the Linux kernel but I couldn’t explain it or knew where to get started with it so I figured I document what we observed and how we got us out of the situation.
15.10.2025
Cups Print Server on Raspberry Pi Timeouts
A few months ago the HP printer my parents were using quit working due to a driver issue. It seems that it is old enough that Apple as well as Microsoft pulled some kind of automatic AirPrint driver discovery deal which rendered the thing useless. For a while they were able to still print from their phones but no desktop computer in the house felt like talking to it anymore.
Given that I do computers, and are seemingly also stupid and refuse to learn from my mistakes, I was convinced I could help them nurse this deal along until the newly acquired ink cartridges were all used up. I did what any self-respecting nerd would do and hooked up yet another Raspberry Pi up to their network and installed the phenomenal cups printing server on it.
I was indeed able to revitalize the printer, at least for a little bit. It kept on seemingly “disconnecting” or “timing-out” after a handful of days without any errors in any logs. I tried to fix it with all kinds of various solutions. I disabled all the power saving modes, tried to come up with all kinds of rain dances in order for my parents to help themselves. As you may already guess, none of it worked.
Just now while fiddling with it again I was presented by an interesting error message in macOS in which it told me that it could discover the printer but not actually connect to the device raspberrypi.local. I was convinced that I had changed the hostname on the device but apparently not well enough as our router was also still convinced that there were multiple local devices with the hostname raspberrypi.local. At this point it hit me that AirPrint relies entirely on Bonjour or LAN/local discovery! If you have more than one host with the same hostname in the network there is a namespace collision and it might work, or it might not, or who knows what kind of cursed undefined and seemingly undocumented behavior any given implementation decides to follow through with.
Logged into Raspberry Pi OS I entered sudo raspi-config and changed the hostname to cups, installed updates while I was already in there and rebooted the host. Once the Pi was responding on the network again I checked macOS which immediately advertised a new HP printer with a @ cups suffix. Trying to setup the printer also worked first try without any issues.
TLDR: make sure that if you want to reliably run the cups printing server on a Raspberry Pi that you give it a unique hostname within your network.
Somehow it is the year 2025 and we’re still partying (😭) like it is 1994. Linux on the “desktop” to the rescue, I hope that this will be my last battle with this system
16.06.2025
How To Verify and Change the Certbot Authenticator
I have never acquired a paid SSL certificate in my life back when it was still SSL and even during my various jobs I never had a reason to obtain a TLS certificate with money, and I may never have to. Prior to the Snowden/Wikileaks events the movement to encrypt the entire internet was already well underway by people who grasped what we were up against and I had heard rumblings about completely free TLS certificates. I can’t recall the exact order in history to be honest as I was very far removed from all of that but one of the results of all of this was the creation of Let’s Encrypt, the certbot project and the ACME protocol.
Fast forward to today and we’re living & breathing Let’s Encrypt and certbot at work. I recently had to consolidate multiple instances of the same project which were setup many years apart to use the exact same configuration just to retain a little bit of our sanity during daily operations. Part of that was that the certbot configuration was different across these environments and I found myself struggling to remember which environment used which certbot authenticator to obtain it’s TLS certificate. I used to like the webroot authenticator and having certbot write the ACME verification challenge into a directory in the filesystem from which the rest of the website was served from as I heavily rely on hugo for everything website related. It was just another static file served by nginx.
I have since come around to using the standalone authenticator though alongside the --http01_port=xxxx flag to have certbot serve the ACME challenge out of RAM in order to eliminate a whole swath of ACL related issues in the future.
In order to check which authenticator is currently used, you need to read the certbot config file from the hostname you’re after in /etc/letsencrypt/renewal/, which should look something like this:
# renew_before_expiry = 30 days
version = 1.12.0
archive_dir =
cert =
privkey =
chain =
fullchain =
# Options used in the renewal process
[renewalparams]
account =
http01_port = 9090
authenticator = standalone
server = https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
key_type = ecdsa
Key things to look out for here is the authenticator value and the related metadata given your authenticator of choice.
Changing Authenticators
Given that you have now looked at your authenticator in horror on some old host and want to change it I have found this great post.
The recommended way to change authenticators is to re-run the certbot command to issue a certificate for the exact same hostname with but including the --force-renewal flag as well. For example
$ certbot certonly --force-renew --standalone -d <your-hostname> --non-interactive --agree-tos --email <your-email-to-be-notified-about-stuff> --http01_port=9090
07.01.2024
E-Mail Server Update
Quite a while ago I wrote about my use of the OSX Server application as I was one of the few remaining people on the internet dumb enough to run my own E-Mail server. Operating this service mostly for myself has taught me a lot which allows me to confidently approach certain problems while helping to develop & run Guardian’s many backend services today for our customers. The broken Mac mini resides on my desk to this day as a reminder of where this journey started.
After shopping around many E-Mail server options, I ultimately landed on Mailcow and I could not be happier about it! Using Docker to solve the problem of making the various components talk to each other was quite intimidating to me at first, as I was afraid about the networking aspect of it all. It turns out though that the maintainers of the project have done a phenomenal job of getting all the various pieces to talk to each other and effortlessly upgrade to newer versions. I suspect the project’s use of Docker is how it was imagined to be used by it’s creators and Mailcow’s setup has become my personal measuring stick whenever I see others trying to leverage Docker as a growth-hacking-problem-abstraction-layer.
Out with the old
As part of my yearly tradition of tinkering with my own hardware over the holiday season I decided that this year was going to be the year to upgrade the servers hardware. I settled on jumping from an Intel i5 6600 to an AMD Ryzen 5 5600G, alongside a new motherboard, new faster RAM etc…
As part of the upgrade I had also decided to jump from running everything bare metal with the desktop variant of Ubuntu 22.04 LTS to Proxmox VE 8 as the primary operating system in order to leverage ZFS and mirrored boot drives as an operational safety net. I have been a ZFS advocate for a few years now and have been fortunate enough to have gained a lot of real world experience with this exact setup. ZFS is the real deal and I will go out of my way to recommend it whenever applicable!
The Mailcow server itself is running the server variant of Ubuntu 22.04 LTS inside a VM managed by Proxmox. All in all things are bit more folded into itself as I added yet another level of abstraction but the Linux Kernel virtualisation layer (KVM) is simply amazing, so none of that ended up giving me any trouble at all!
As part of the takedown preparation of the old server I ran a backup of the E-Mail inboxes itself with imapsync (link) followed by a complete backup with Mailcow’s backup-and-restore (link) script. The output of that script are a bunch of .tar.gz files as well as the Mailcow configuration file which I rsync’d to the new Mailcow VM. The same backup-and-restore script was run in the VM to restore a one-to-one copy of the old on the new server and I was back up and running within a bit over an hour end-to-end.
No E-Mail client that interacts with my server appears to have noticed anything about the move, which has done nothing but push my confidence in the Mailcow toolchain even further. If you think about running your own E-Mail server for whatever reason, Mailcow would be my recommendation 10/10 times!
One key thing that I am still missing in Mailcow is the XAPPLEPUSHSERVICE which was a Apple created custom Dovecot extension in OSX Server, to enable you to send push notifications about new E-Mail to iOS’s Mail.app. So far the only other provider being able to do this has been Fastmail to my knowledge, but I am not entirely sure whether they support it anymore as I have not been able to get it to work recently with my Fastmail account.
31.12.2023
Being A Good Citizen on the Internet
I must admit that I am severely impressed. Whenever I think of Backblaze at this point I think of a size-able company, maintaining EXABYTES (that number makes no sense whatsoever) of data from individuals as well as massive corporations. They run two physical locations with lots of staff and develop their own hardware & software to make all of this happen while being entirely independent of the few big “cloud” providers that have cornered the market.
This mentality is something I have always looked up to and am actively pursuing with my work at Guardian, which is now part of DNSFilter. If you want it to be done correctly you either resort to buying the most expensive option, which you probably can’t afford and is not guaranteed to solve your problem, or do it yourself. For a lot of problems those are the two options if you want to avoid mediocre, middle-of-the-road crap. Backblaze has mostly chosen to do the latter, which is something that I can really respect.
Given their responsibilities and reputation I was quite impressed to see a seemingly real human being reach out to me via E-Mail, kindly asking me to update an older link on my tiny website to their B2 product. I was going to write back telling them that I would do that but that they should ensure that they have forwards setup for the old links, but as I tested that I quickly noticed that they were already way ahead of me.
This is how you do PR work correctly for a company of any size! No ego & no weird lawyerly phrasing, just a regular message from somebody reaching out kindly asking to avoid a redirect for anybody clicking the link on my website. Backblaze has once again proven that the organization as a whole has not fallen into the
“big corporation that is required to increase shareholder value by any means”
trap and is aware that they’re just a citizen of the internet like any of us. And they’re making an effort trying to be a good internet citizen, too! I am still dearly missing a few (basic-ish) features which I would expect from their product to further integrate it into Guardian itself, but this interaction has once again proven that Backblaze is a great company to be a customer of and has really re-assured my trust in them with regards to everything that they do. I would love to one day be able to tour one of their facilities, given that I have followed their lead with building backup servers out of cheap components and being successful at it.
None of this was related to their technical strategy, past decisions or current offering, but solely on a normal human interaction.
Funny how effective a little bit of politeness & self-awareness is in this anonymized, digital world…
06.08.2023